Learn About Cannabigerol CBG
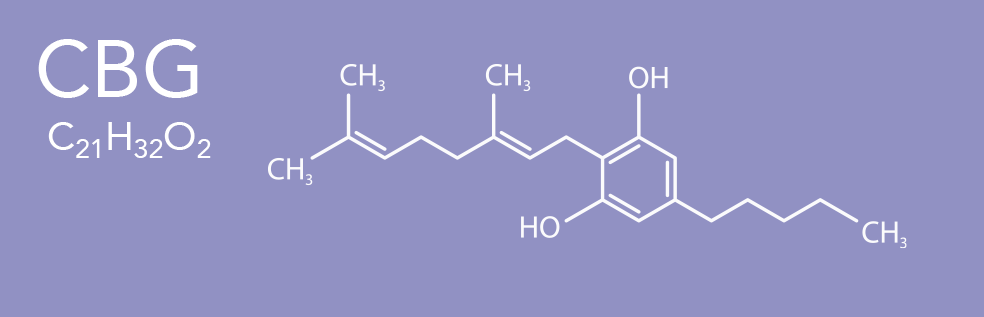
Cannabigerol CBG is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus Cannabis. Cannabigerol is the decarboxylated form of Cannabigerolic Acid CBGa, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized. Cannabigerol is a rare cannabinoid that is a minor constituent of cannabis. During plant growth, most of the cannabigerol is converted into other cannabinoids, primarily tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) or cannabidiol (CBD), leaving about 1% cannabigerol in the plant.
Like THC, CBG reacts with the cannabinoid receptors in the brain. CBG, however, acts as a buffer to the psychoactivity of THC by working to alleviate the paranoia sometimes caused by higher levels of THC. Clinical research reveals that CBG works to fight inflammation, pain, nausea and works to slow the proliferation of cancer cells. Research has also shown it to significantly reduce intraocular eye pressure caused by glaucoma. Strains high in CBG may be beneficial treating conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, and cancer.
CBG acts as a low-affinity antagonist at the CB1 receptor. CBG pharmacological activity at the CB2 receptor is currently unknown. CBG’s antibacterial effects can alter the overall effects of cannabis. CBG is known to kill or slow bacterial growth, reduce inflammation, (particularly in its acidic CBGA form,) inhibit cell growth in tumor/cancer cells, and promote bone growth.
Another effect CBG has on the brain is that it inhibits the uptake of GABA, a brain chemical that determines how much stimulation a neuron needs to cause a reaction. When GABA is inhibited it can decrease anxiety and muscle tension similar to the effects of cannabidiol (CBD).
When ingested orally, CBG can produce an energetic feeling (referred to by some as a "body high"). Common delivery systems for CBG-rich products are primarily tinctures and gummies.
Cannabinoids Knowledgebase

Cannabigerol Clinical Research
Benefits of VCE-003.2, a cannabigerol quinone derivative, against inflammation-driven neuronal deterioration in experimental Parkinson’s disease: possible involvement of different binding sites at the PPARγ receptor
Concepción García, María Gómez-Cañas, Sonia Burgaz, Belén Palomares, Yolanda Gómez-Gálvez, Cristina Palomo-Garo, Sara Campo, Joel Ferrer-Hernández, Carolina Pavicic, Carmen Navarrete, M. Luz Bellido, Moisés García-Arencibia, M. Ruth Pazos, Eduardo Muñoz, Javier Fernández-Ruiz | Journal of Neuroinflammation Volume 15, Article No: 19 (2018) | Full Text
Colon carcinogenesis is inhibited by the TRPM8 antagonist cannabigerol, a Cannabis-derived non-psychotropic cannabinoid
Francesca Borrelli, Ester Pagano, Barbara Romano, Stefania Panzera, Francesco Maiello, Diana Coppola, Luciano De Petrocellis, Lorena Buono, Pierangelo Orlando, Angelo A. Izzo | Carcinogenesis, Volume 35, Issue 12, December 2014 | Full Text
Beneficial effect of the non-psychotropic plant cannabinoid cannabigerol on experimental inflammatory bowel disease
Francesca Borrellia, Ines Fasolino, Barbara Romano, Raffaele Capasso, Francesco Maiello, Diana Coppola, Pierangelo Orlando, Giovanni Battista, Ester Pagano, Vincenzo Di Marzo. Angelo A. Izzo | Biochemical Pharmacology Volume 85, Issue 9, 1 May 2013, Pages 1306-1316 | Full Text
A Cannabigerol Quinone Alleviates Neuroinflammation in a Chronic Model of Multiple Sclerosis
Aitor G. Granja, Francisco Carrillo-Salinas, Alberto Pagani, María Gómez-Cañas, Roberto Negri, Carmen Navarrete, Miriam Mecha, Leyre Mestre, Bend L. Fiebich, Irene Cantarero, Marco A. Calzado, Maria L. Bellido, Javier Fernandez-Ruiz, Giovanni Appendino, Carmen Guaza, Eduardo Muñoz | Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology Volume 7, pages 1002–1016 (2012) | Full Text
Evidence that the plant cannabinoid cannabigerol is a highly potent α2-adrenoceptor agonist and moderately potent 5HT1A receptor antagonist
MG Cascio, LA Gauson, LA Stevenson, RA Ross, RG Pertwee | January 19, 2010 | British Journal of Pharmacology | Full Text

