Cannabinol (CBN)
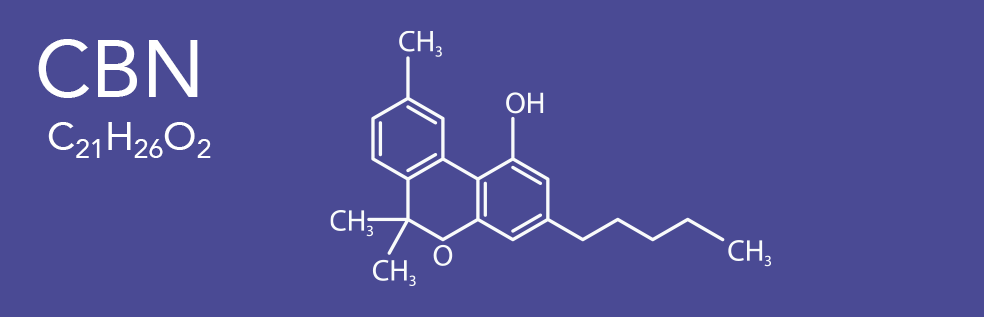
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid found in trace amounts in Cannabis sativa. CBN is mostly found in cannabis that is aged and stored, and is derived from the plant's main psychoactive chemical, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). CBN was the first cannabis compound to be isolated from cannabis extract in the late 1800s. Then by the 1930s, the first to have its structure determined and in 1940, to have scientists achieve its chemical synthesis.
CBN acts as a weak agonist at both the CB1 and CB2 receptors, with greater affinity for CB2 receptors than CB1. The degradation of THC into CBN is often described as creating a sedative effect, known as a “couch lock”. For this reason, CBN is widely referred to as "the sleep molecule".
The research on cannabinol (CBN) is still lacking, but some early studies have suggested it could stimulate bone growth. If that’s the case, it would be helpful in treating osteoporosis. It may also help those with broken bones to recover more quickly. This cannabinoid has also been shown in studies to help regulate the immune system and works to relieve the pain and inflammation caused by several conditions, including arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Other studies show that it can be used to reduce the intraocular eye pressure caused by glaucoma. CBN acts as an anticonvulsant, so it is also beneficial to patients suffering from seizure disorders including epilepsy.
Cannabinoids Knowledgebase
- Cannabinoids 101
- The Endocannabinoid System
- The Entourage Effect
- About Cannabidiol (CBD)
- About Cannabidiolic Acid (CBDa)
- About Cannabigerol (CBG)
- About Cannabigerolic Acid (CBGa)
- About Cannabinol (CBN)
- About Cannabichromene (CBC)
- About Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
- About Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV)
- About Terpenes & Terpenoids

Cannabinol Clinical Research
Potential Use of Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
Golnaz Sharafi, Hong He, Mehrdad Nikfarjam | January 25, 2019 | Journal of Pancreatic Cancer Volume 5, Number 1 | Full Text
Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: a structure-activity study
Giovanni Appendino, Simon Gibbons, Anna Giana, Alberto Pagani, Gianpaolo Grassi, Michael Stavri, Eileen Smith, M Mukhlesur Rahman | August 2006 | Journal of Natural Products | Full Text
Turning Over a New Leaf: Cannabinoid and Endocannabinoid Modulation of Immune Function
Guy A. Cabral, Thomas J. Rogers, Aron H. Lichtman | June 9, 2015 | Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology | Full Text

